Benign laryngeal tumors are non-cancerous throat tumors that develop in the larynx (voice box). While these growths are not cancerous and do not spread to other parts of the body, they can lead to significant voice and throat issues. Unlike malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign laryngeal tumors are generally less dangerous but require early diagnosis and treatment to avoid complications such as hoarseness and vocal cord damage. In this blog, we will explore the causes, and symptoms of benign laryngeal tumors, diagnosis, and treatment options for benign laryngeal tumors to help you understand how to manage this condition effectively.
What Are Benign Laryngeal Tumors?
Benign laryngeal tumors are non-cancerous throat tumors that form in the larynx or voice box. These tumors are typically caused by prolonged irritation or injury to the vocal cords, which leads to changes in the tissue. The term “benign” refers to the fact that these growths do not spread to other parts of the body, unlike malignant tumors, which can be cancerous.
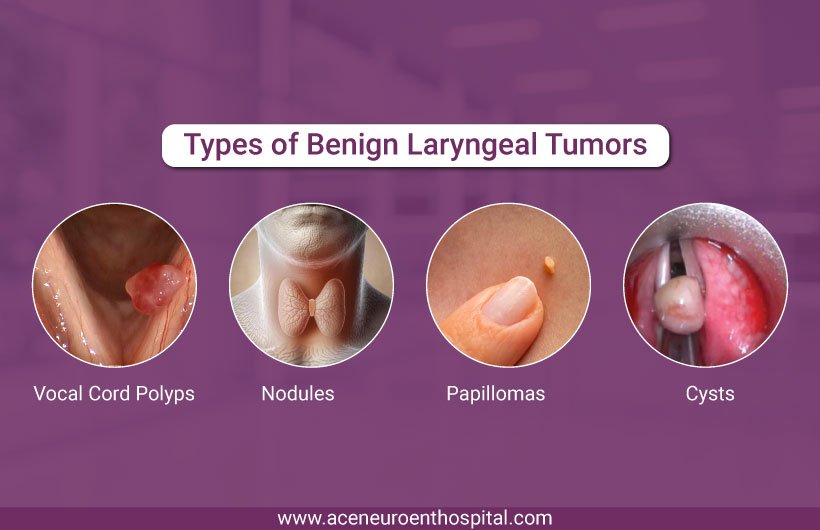
Common types of benign laryngeal tumors include:
- Vocal cord nodules: These are often caused by overuse or strain on the voice and are commonly seen in professions such as teaching, singing, or public speaking.
- Polyps: Fluid-filled growths that can develop on the vocal cords due to vocal trauma or irritation.
- Papillomas: These growths are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) and are typically wart-like structures that form on the vocal cords and larynx.
- Cysts: These occur when the mucus glands in the larynx become blocked, leading to cyst formation.
While these non-cancerous throat tumors are generally not harmful, they can cause significant disruptions in vocal function, and treatment is often necessary.
Causes and Risk Factors
Benign laryngeal tumors can result from various causes and risk factors. Some of the most common causes include:

Common Causes:
- Chronic voice strain: Professions or activities that require frequent or loud vocalizations, such as teaching, singing, or public speaking, can lead to vocal cord damage and increase the risk of developing benign laryngeal tumors.
- Acid reflux (Laryngopharyngeal reflux – LPR): Stomach acid that travels into the throat can irritate the vocal cords and lead to the formation of non-cancerous throat tumors.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection: This viral infection is a significant cause of papillomas, a specific type of benign laryngeal tumor.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol use can irritate the vocal cords and increase the risk of developing benign laryngeal tumors.
- Environmental irritants: Exposure to pollutants or chemicals, whether at work or in the environment, can lead to irritation and non-cancerous throat tumors.
Who Is at Risk? Certain individuals are more likely to develop benign laryngeal tumors, including:
- People with frequent throat infections: Regular infections can weaken the vocal cords, making them more susceptible to developing benign laryngeal tumors.
- Those with poor vocal hygiene: Failing to take care of your voice can lead to vocal cord damage and benign laryngeal tumors.
- Individuals with chronic acid reflux: People with LPR may experience constant irritation of the vocal cords, leading to non-cancerous throat tumors over time.
Symptoms of Benign Laryngeal Tumors
The symptoms of benign laryngeal tumors can vary depending on the size, type, and location of the tumor. Some common early signs include:
- Persistent hoarseness or voice changes: A raspy, weak, or strained voice is often an early sign of a benign laryngeal tumor affecting the vocal cords.
- Sore throat or discomfort when speaking: Tumors in the larynx can cause pain or irritation when speaking or swallowing.
- Feeling of a lump in the throat: Many people with non-cancerous throat tumors report the sensation of something being stuck in their throat.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia): Large tumors can make swallowing food or liquids difficult and uncomfortable.
- Chronic cough or throat clearing: A persistent need to clear your throat or a lingering cough could signal a benign laryngeal tumor.
When to See a Doctor? If you experience these symptoms for more than 2-3 weeks, or if you have trouble breathing or a significant loss of your voice, it’s important to consult a doctor. Early diagnosis of benign laryngeal tumors can prevent further complications.
How Are Benign Laryngeal Tumors Diagnosed?
To diagnose benign laryngeal tumors, your doctor will perform a comprehensive medical examination. This may include:
- Laryngoscopy: A fiber-optic camera is used to view the larynx and assess any abnormalities in the vocal cords.
- Stroboscopy: This technique evaluates the vibrations of the vocal cords to understand how well they are functioning.
- Biopsy: If necessary, a small tissue sample may be taken to confirm that the tumor is benign and not cancerous.
Imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRIs, may also be used to determine the size, location, and nature of the tumor, aiding in treatment planning.
Treatment Options for Benign Laryngeal Tumors
The treatment for benign laryngeal tumors depends on factors such as the size, type, and symptoms caused by the tumor. Treatment options for benign laryngeal tumors include both non-surgical and surgical methods.
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Voice therapy: Speech therapy is often used to teach patients how to properly use their voice, reducing strain and preventing further damage to the vocal cords.
- Lifestyle changes: Staying hydrated and avoiding smoking and alcohol can help reduce irritation of the vocal cords and prevent further development of benign laryngeal tumors.
- Acid reflux management: Medications and dietary changes can help manage acid reflux, preventing further damage to the vocal cords and reducing the risk of non-cancerous throat tumors.
Surgical Treatments (for larger or symptomatic tumors):
- Microlaryngoscopy: This minimally invasive procedure allows for the removal of tumors with small instruments, causing minimal damage to the vocal cords.
- Laser surgery: Laser treatment is precise and can remove benign laryngeal tumors with minimal damage to the surrounding tissue.
- Cryotherapy: This technique uses extreme cold to freeze and remove non-cancerous throat tumors.
Post-Treatment Care: Following treatment, it is crucial to rest the voice, stay hydrated, and attend follow-up appointments to monitor for tumor recurrence.
How to Prevent Benign Laryngeal Tumors?
Preventing benign laryngeal tumors primarily involves maintaining proper vocal health and avoiding environmental irritants. Here are some tips to reduce the risk:
- Vocal hygiene: Avoid excessive shouting and take frequent breaks to rest your voice, especially if you use it heavily.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep the vocal cords moist and use a humidifier if you live in a dry environment.
- Dietary & Lifestyle Adjustments: Managing acid reflux through diet, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol consumption can significantly lower the risk of developing non-cancerous throat tumors.
Can a Benign Laryngeal Tumor Become Cancerous?
While the risk of benign laryngeal tumors turning cancerous is low, it is important to monitor any growths regularly. If a tumor changes in size, appearance, or causes persistent pain, it may require reevaluation by a healthcare provider. Regular check-ups are essential for early detection if any changes occur.
Conclusion
Benign laryngeal tumors, although non-cancerous throat tumors, can lead to significant voice and throat problems if not treated properly. Understanding the causes, and symptoms of benign laryngeal tumors, and treatment options can help you manage the condition effectively. If you experience persistent throat discomfort or voice changes, seek medical evaluation from an ENT specialist in Ahmedabad like Dr Simple Bhadania, who can provide a thorough assessment and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Experiencing prolonged voice changes or throat discomfort? Consult an ENT specialist today for a thorough evaluation.


